Artificial Intelligence (AI) chatbots have become increasingly prevalent, powering everything from customer service to virtual personal assistants. They help businesses automate interactions, provide instant responses, and enhance user engagement. Yet, many people—especially those without a technical background—wonder how these chatbots actually work. This detailed guide breaks down the complex technology behind AI chatbots into simple, understandable concepts, empowering readers to appreciate how chatbots operate and how non-developers can leverage them effectively.
Table of contents:
- What Are AI Chatbots?
- How Do AI Chatbots Work? Step-by-Step
- Core Technologies Behind AI Chatbots
- Common Uses and Applications
- Benefits of AI Chatbots for Non-Developers
- How Non-Developers Can Use or Build AI Chatbots
- Common Misconceptions
- Future Trends in AI Chatbots
- Conclusion
What Are AI Chatbots?
At their core, AI chatbots are computer programs programmed to simulate human conversation. More than just simple automated responders, modern chatbots use sophisticated AI algorithms to understand context, intent, and sentiment, enabling natural, interactive dialogues with users.
There are two broad categories:
- Rule-Based Chatbots: Operate by following predefined rules and scripted responses. They trigger responses based on keywords or fixed phrases and are best suited for handling straightforward, repetitive queries.
- AI-Powered Chatbots: Use artificial intelligence, particularly machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP), to interpret user inputs dynamically. They learn from interactions, improve over time, and can manage complex, open-ended conversations.
Get a free AI chatbot consultation with Zeevium today: https://zeevium.com
How Do AI Chatbots Work? Step-by-Step
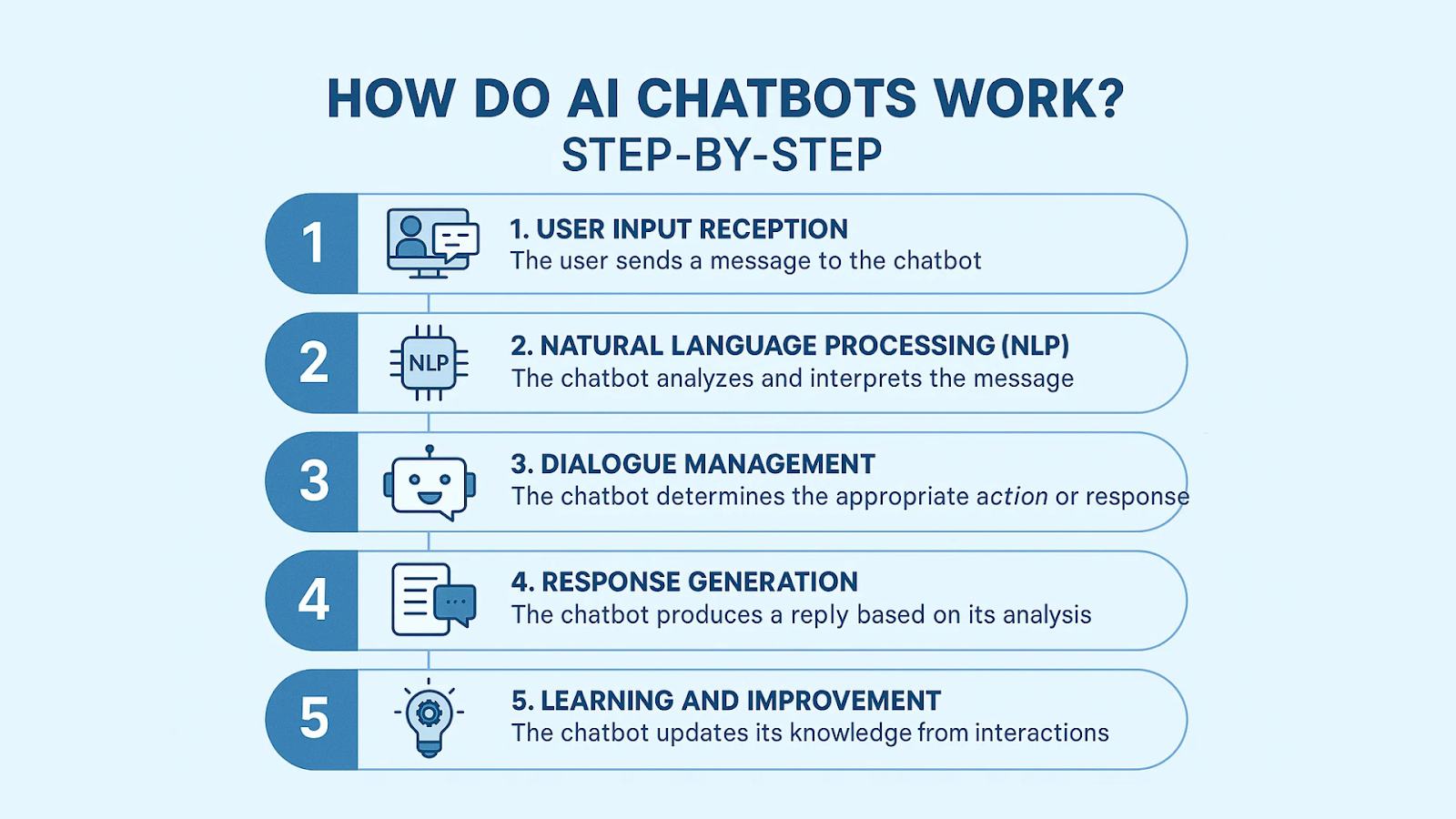
1. User Input Reception
Chatbots receive input from users via text (chat windows, messaging apps) or voice commands (smart speakers, phones). This input is captured and transformed into machine-readable text for analysis. For voice input, speech-to-text algorithms convert spoken words into text.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP is the AI branch that enables machines to understand human language. This involves several sub-steps:
- Intent Recognition: Determining what the user wants to achieve (e.g., booking a ticket, asking a question).
- Entity Extraction: Pulling out specific data points from the input such as dates, locations, names, or product details.
- Sentiment Analysis: Optional but important; determining the emotional tone behind the user’s words (anger, happiness, urgency).
Example: For “I want to book a flight to Singapore next Monday,” the intent is booking a flight, with entities ‘Singapore’ and ‘next Monday’.
3. Dialogue Management
Based on the interpreted input, the chatbot decides how to respond. The dialogue manager uses conversation context and rules or AI models to determine the appropriate next step:
- Retrieve information from a database or external API.
- Ask clarifying questions.
- Provide direct answers.
- Escalate to a human agent if necessary.
4. Response Generation
AI chatbots generate responses either by fetching pre-written replies or dynamically creating them using advanced language models like GPT or BERT. The goal is to produce natural, coherent, and contextually relevant sentences.
5. Learning and Improvement
Each interaction is logged and analyzed for performance. Using machine learning, chatbots improve over time, refining intent recognition, response accuracy, and conversation flow. Feedback loops, user ratings, and conversational analytics are key components.
Core Technologies Behind AI Chatbots
- Machine Learning (ML): Algorithms that enable chatbots to learn from data and improve without explicit programming.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Technology that translates human language into data the chatbot can understand and act on.
- Deep Learning & Neural Networks: Used in advanced chatbots to understand context and subtle nuances in language.
- Speech Recognition & Synthesis: Allow voice interaction via speech-to-text and text-to-speech systems.
Common Uses and Applications
- Customer Service: Automating FAQs, complaints, booking, and payment processes with instant replies.
- E-Commerce: Guiding shoppers, recommending products, and processing orders.
- Education: Virtual tutors providing personalized learning assistance.
- Healthcare: Symptom checking, appointment management, and patient education.
- Entertainment: Storytelling, trivia games, and interactive companions.
- Internal Business Tools: Onboarding, IT help desks, and HR inquiries.
Benefits of AI Chatbots for Non-Developers
- 24/7 Availability: Never sleeps, providing instant answers anytime.
- Cost-Efficiency: Reduces need for large customer service teams.
- Scalability: Handles many users simultaneously.
- Personalization: Offers tailored responses based on user history or preferences.
- Ease of Use: Many platforms allow setting up chatbots with minimal technical skills via drag-and-drop interfaces.
How Non-Developers Can Use or Build AI Chatbots
Thanks to modern platforms, setting up or customizing chatbots no longer demands coding expertise:
- No-Code/Low-Code Platforms: Services like Chatfuel, ManyChat, or Microsoft Power Virtual Agents enable building chatbots using graphical interfaces and templates.
- Pre-Trained Models: Use AI models trained on general conversation datasets, customizable for specific business needs.
- Integration with Popular Channels: Easily connect chatbots to Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, websites, or mobile apps.
- Analytics & Optimization Tools: Monitor chatbot interactions and tweak responses using dashboard insights.
Common Misconceptions
- “Chatbots are robotic and unnatural.” Modern AI chatbots can produce responses that feel conversational and context-aware.
- “You need to be a programmer.” Many tools simplify creation for marketers, customer service managers, and business owners.
- “Chatbots replace humans entirely.” In truth, they handle routine queries and escalate complex cases to humans, enhancing overall service efficiency.
Future Trends in AI Chatbots
- Multimodal Interaction: Combining voice, text, images, and video for richer conversations.
- Emotional AI: Understanding and responding to user emotions more effectively.
- Deep Personalization: Chatbots that maintain detailed user profiles and context across platforms.
- Conversational Commerce: Seamless transactions initiated and completed entirely through chatbots.
- Integration with Other AI: Combining chatbots with AR/VR and IoT devices for immersive experiences.
Conclusion
AI chatbots are sophisticated yet accessible tools that transform how businesses communicate and engage with users. Even without being a developer, anyone can understand their core workings and leverage user-friendly platforms to deploy powerful chatbots tailored to their needs. As AI and NLP technologies evolve, chatbots will continue becoming smarter, more human-like, and indispensable in many sectors.
Let’s connect with Zeevium to establish your first AI chatbot. Zeevium specializes in AI solutions, guiding you to integrate cutting-edge chatbots tailored to your specific business needs. They focus on customized development that reflects your brand’s voice and goals, ensuring seamless integration with your existing platforms. With Zeevium, you get expert consultation, an accessible deployment process even if you’re not a developer, and ongoing support to keep your chatbot effective and evolving.
